Octelium supports Authenticators since version v0.21.0. There are currently three types of Authenticators:
-
FIDO Used by FIDO/WebAuthn compliant authenticators such as security keys (e.g. Yubikey), hardware-backed platform authenticators (e.g. Windows Hello, Android) and software-based keys (e.g. Google Password Manager). FIDO Authenticators can be used for both MFA after a successful IdentityProvider authentication, manual re-authentication for existent browser-based Sessions, as well as for direct passwordless login via Passkeys.
-
TOTP Time-based one-time password (TOTP) Authenticators can be using via apps such as Google Authenticator for MFA right after a successful IdentityProvider authentication as well as for re-authentication for both browser-based Sessions as well as for
CLIENT-based Sessions used by theocteliumandocteliumctlCLIs. -
TPM This Authenticator uses TPM (Trusted Platform Module) 2.0 to provide hardware-based re-authentication for
CLIENT-based Sessions used by theocteliumandocteliumctlCLIs. This Authenticator currently works forLINUXandWINDOWSDevices.
Listing Authenticators
You can list the Cluster's Authenticators (read more about listing resources here) as follows:
octeliumctl get authenticator# Or simplyocteliumctl get authn# List Authenticators filtered by a certain Userocteliumctl get authn --user john# Show a certain IdentityProviderocteliumctl get authn <NAME>
Authentication Enforcement Rules
By default, once Users authenticate themselves via a web-based IdentityProvider, their Session is considered valid and can be used to access the authorized Services without enforcing MFA via Authenticators. You can, however, override that behavior and explicitly require Authenticator authentication as MFA right after a successful IdentityProvider authentication via the authenticationEnforcementRules list. Each rule has a condition and an effect that is set to either ENFORCE to enforce/require the Authenticator authentication, RECOMMEND or IGNORE to require/ignore enforcement on the condition match. Here is an example:
1kind: ClusterConfig2metadata:3name: cluster-config4spec:5authenticator:6authenticationEnforcementRules:7- condition:8match: ctx.user.spec.email.endsWith("@example.com")9effect: ENFORCE10- condition:11match: '"friends" in ctx.user.spec.groups'12effect: IGNORE13- condition:14match: ctx.session.status.isBrowser15effect: ENFORCE16- condition:17match: ctx.identityProvider.status.type in ["SAML", "OIDC"]18effect: RECOMMEND
Registration Enforcement Rules
By default, the Cluster does not try to force Users to enroll Authenticators after a successful web-based login via an IdentityProvider. You can, however, override that behavior and dynamically require an Authenticator registration based on identity and/or context via the registrationEnforcementRules list. Each rule has a condition and an effect that is set to either ENFORCE, RECOMMEND or IGNORE to require/ignore enforcement on the condition match. Here is an example:
1kind: ClusterConfig2metadata:3name: cluster-config4spec:5authenticator:6registrationEnforcementRules:7- condition:8match: ctx.user.spec.email.endsWith("@example.com")9effect: ENFORCE10- condition:11match: size(ctx.authenticatorList.items) == 012effect: ENFORCE13- condition:14match: '"friends" in ctx.user.spec.groups'15effect: IGNORE16- condition:17match: ctx.identityProvider.status.type in ["SAML", "OIDC"]18effect: RECOMMEND
Post Authentication Rules
By default, a Session is created on a valid login and re-validated on a successful re-authentication. However, you can override that behavior and deny a successful Authenticator authentication based on identity and context via the postAuthenticationRules list. For example, you might want to prevent more privileged Users from using TOTP Authenticators and only allow them to authenticate via hardware-based FIDO2 security keys. You can also prevent authentications on a certain time and day. Here is an example:
1kind: ClusterConfig2metadata:3name: cluster-config4spec:5authenticator:6postAuthenticationRules:7- condition:8match: ctx.authenticator.status.type == "TOTP"9effect: DENY10- condition:11all:12of:13- match: ctx.user.spec.groups.hasAny(["dev", "ops"])14- match: ctx.session.status.isBrowser15- not: ctx.authenticator.status.info.fido.isAttestationVerified16effect: DENY17- condition:18all:19of:20- match: ctx.session.status.isBrowser21- not: ctx.authenticator.status.info.fido.isHardware22effect: DENY
FIDO
Attestation
During the registration process of a FIDO Authenticator, the Authenticator attestation, if provided in the registration ceremony response, is verified against the MDSv3 blob maintained by FIDO Alliance (read more about WebAuthn attestation here). You can use such information in your Policies' access control decisions as shown below here, for example, to verify that the authentication is made by a genuine hardware-backed Authenticator and additionally force a list of allowed manufacturer AAGUIDs.
Passkey Login
By default, the ability to login with Passkeys is not enabled. You can explicitly enable it in the ClusterConfig as follows:
1kind: ClusterConfig2metadata:3name: cluster-config4spec:5authenticator:6enablePasskeyLogin: true
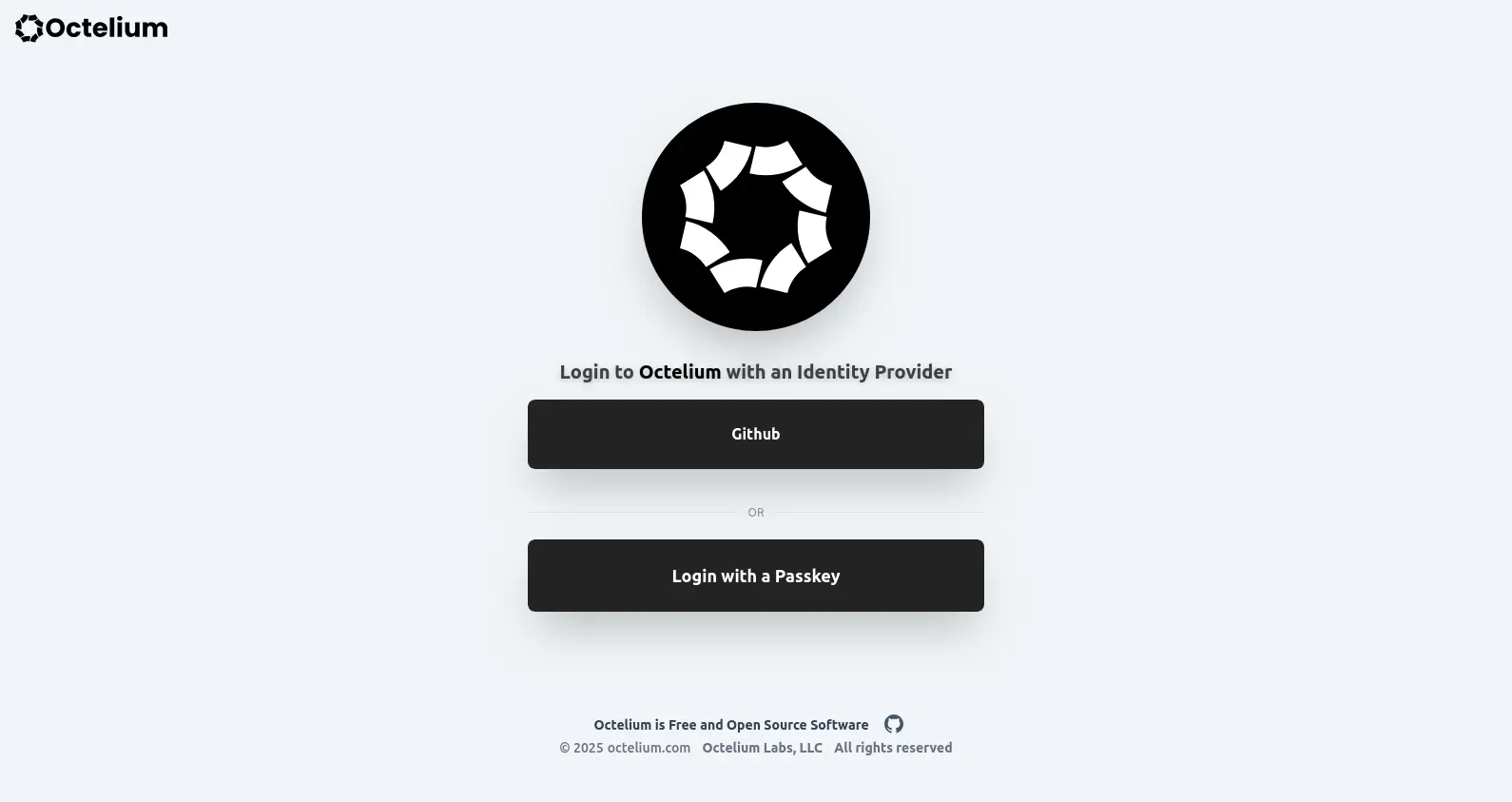
Now any registered FIDO Authenticator that supports resident key credentials can be used for Passkey login. Once enabled by setting enablePasskeyLogin, your Cluster's login page will show a "Login with a Passkey" button as shown below.
Attestation Conveyance Preference
By default, Octelium uses DIRECT attestation (read more here). You can, however, override that default preference and use INDIRECT, ENTERPRISE or NONE attestation conveyance preferences. Here is an example:
1kind: ClusterConfig2metadata:3name: cluster-config4spec:5authenticator:6fido:7attestationConveyancePreference: INDIRECT
Access Control
You can control use the current Authenticator information in your Policies' rules to control access to Services. Here is an example where you only allow LINUX or MAC Devices:
1kind: Policy2metadata:3name: allowed-devices4spec:5rules:6- effect: ALLOW7condition:8all:9of:10- match: ctx.session.status.authentication.info.type == "AUTHENTICATOR"11- match: ctx.session.status.authentication.info.authenticator.isAttestationVerified12- match: ctx.session.status.authentication.info.authenticator.isHardware13- match: ctx.session.status.authentication.info.authenticator.userVerified14- match: ctx.session.status.authentication.info.authenticator.userPresent15- match: ctx.session.status.authentication.info.authenticator.aaguid == "cb69481e-8ff7-4039-93ec-0a2729a154a8"
State
A Session has one of 3 states at a time, namely ACTIVE, REJECTED and PENDING as follows:
ACTIVEindicates an active Authenticator.REJECTEDmeans that the Authenticator is simply deactivated and cannot be used for authentication unless the Authenticator is set toACTIVEagain.PENDINGindicates that the Authenticator is still pending for a decision whether to be activated or deactivated orREJECTED.
The Cluster by default automatically sets the state for a newly created Device to ACTIVE. You can explicitly set a default Device state for a specific User (read more here) as follows:
1kind: User2metadata:3name: john4spec:5type: HUMAN6authentication:7defaultAuthenticatorState: ACTIVE
You can also set the default state at the Cluster level via ClusterConfig (read more here), as follows:
1kind: ClusterConfig2metadata:3name: cluster-config4spec:5authenticator:6defaultState: PENDING
Approving Authenticators
You can approve an Authenticator to set its state to ACTIVE simply as follows:
octeliumctl update authn --approve <AUTHENTICATOR_NAME>
Rejecting Authenticators
You can reject an Authenticator to set its state to REJECTED simply as follows:
octeliumctl update authn --reject <AUTHENTICATOR_NAME>